Extract, Transform, Load
Key steps, tools, and best practices of ETL.
What is ETL?
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) is the foundational process behind data integration, ensuring that data from different sources is collected, processed, and made usable for business analysis and decision-making. This process is essential for organizations that handle data from multiple sources and need it compiled into a unified format, such as a database or data warehouse. Each stage of the ETL process serves a distinct function: extracting the raw data, transforming it into a consistent format, and finally loading it into a system where it can be used for reporting or analytics. ETL processes are vital for data consolidation, enabling businesses to leverage their data effectively for insights and strategic planning.
Key Steps
Extract is the first stage, wherein data is collected from various sources such as APIs, file systems, or databases. For example, a company may extract sales data from an online platform, customer information from a CRM system, or financial records from internal databases. The extraction step ensures that data is collected from all necessary locations and is ready for further processing.
In the Transform step, the extracted data undergoes cleaning, filtering, and reformatting to ensure consistency and accuracy. Data transformation is crucial because raw data often contains inconsistencies, errors, or formats that are incompatible with target systems. For instance, customer names may be recorded differently across multiple systems, or dates might need to be standardized. The transformation phase ensures data is coherent and usable, converting it into a format suitable for the target system or analysis.
After the data has been transformed, the final step is to Load it into a target system, such as a database, data warehouse, or analytics platform. This step enables the data to be stored in a structured format, allowing easy access for reporting and analysis. A financial company, for instance, may load data into a data warehouse to generate quarterly reports or forecast future trends.
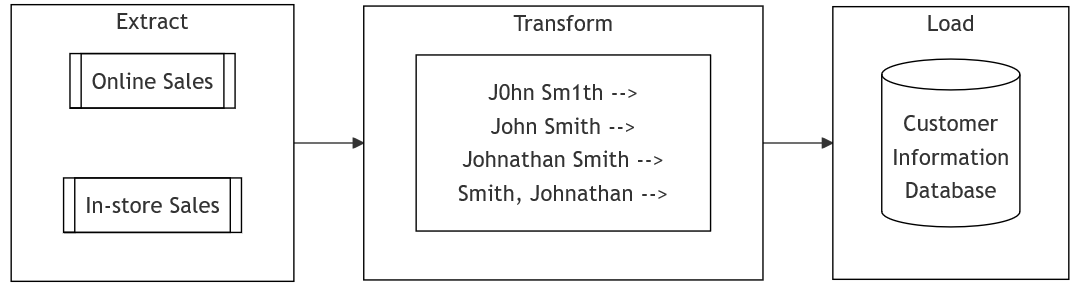
Figure 3: ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Process Example Illustrating Data Integration from Online and In-Store Sales
Tools to Know About
Several tools can automate and optimize the ETL process, reducing manual effort and improving data handling efficiency. These tools range from enterprise-level platforms to more accessible solutions tailored to small businesses.
Popular and Flexible
- Apache Nifi
A powerful platform for automating data flow across multiple systems with real-time processing and a user-friendly interface. Best suited for larger organizations handling complex data streams. - Talend
Offers both open-source and enterprise-grade ETL solutions. Talend supports cloud and on-premises environments, making it a great option for businesses of all sizes. Small businesses can start with the open-source version, while larger enterprises can leverage more advanced features. - Microsoft SSIS
An ETL tool within Microsoft SQL Server, SSIS is perfect for organizations already using Microsoft technologies. It's ideal for enterprises needing strong data transformation capabilities.
Best for Small Businesses
- Zapier
Great for small businesses needing simple workflows between apps like Google Sheets and CRMs, without coding or complex integrations. - Stitch
A lightweight ETL tool for small to mid-sized businesses, focusing on extracting and loading data. It's easy to use and integrates with other transformation tools like dbt. - Fivetran
A fully managed ETL service, ideal for businesses without dedicated IT staff. It automates data extraction and loading from cloud apps and databases.
For Organizations Working in the Cloud
- Matillion
Integrates seamlessly with platforms like Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery. It's easy to use but is limited to cloud use cases, making it ideal for businesses committed to a cloud-first approach. - AWS Glue
Tightly integrated with the AWS ecosystem. It's excellent for companies heavily using AWS services, offering automatic schema discovery and ETL code generation. - Apache Airflow
A leading open-source tool for orchestrating complex workflows. Airflow is great for managing large-scale data pipelines with flexibility, but it requires technical expertise to set up and manage.
Best Practices for ETL
To ensure ETL processes are efficient and reliable, following best practices is essential for maintaining data integrity and performance. During the transformation phase, it's crucial to implement data validation and quality checks to maintain accuracy. This prevents erroneous or corrupted data from being passed downstream and ensures that the final dataset is consistent and trustworthy. Businesses can catch issues early by establishing validation rules—such as range checks, format validations, and duplicate detections.Nonetheless, errors do occur. Businesses need to establish robust error-handling mechanisms across all stages of the ETL process. This should include automated error logging, notifications for critical failures, and fallback strategies to ensure that data pipelines can continue running or recover quickly from interruptions. By managing errors efficiently, data flow can continue without significant delays or data loss.
Finally, ETL processes can be resource-heavy, especially when dealing with large datasets or real-time data streams. Optimizing the performance of ETL pipelines through strategies like batch processing, incremental updates, and using indexed queries can significantly reduce processing time and improve overall system performance. Regular performance monitoring also helps identify bottlenecks and areas for further improvement.
Other Topics in Chapter 3:
Evaluate the Role of Spreadsheets vs. DatabasesLearn How to Scale Data Solutions to the Cloud